1
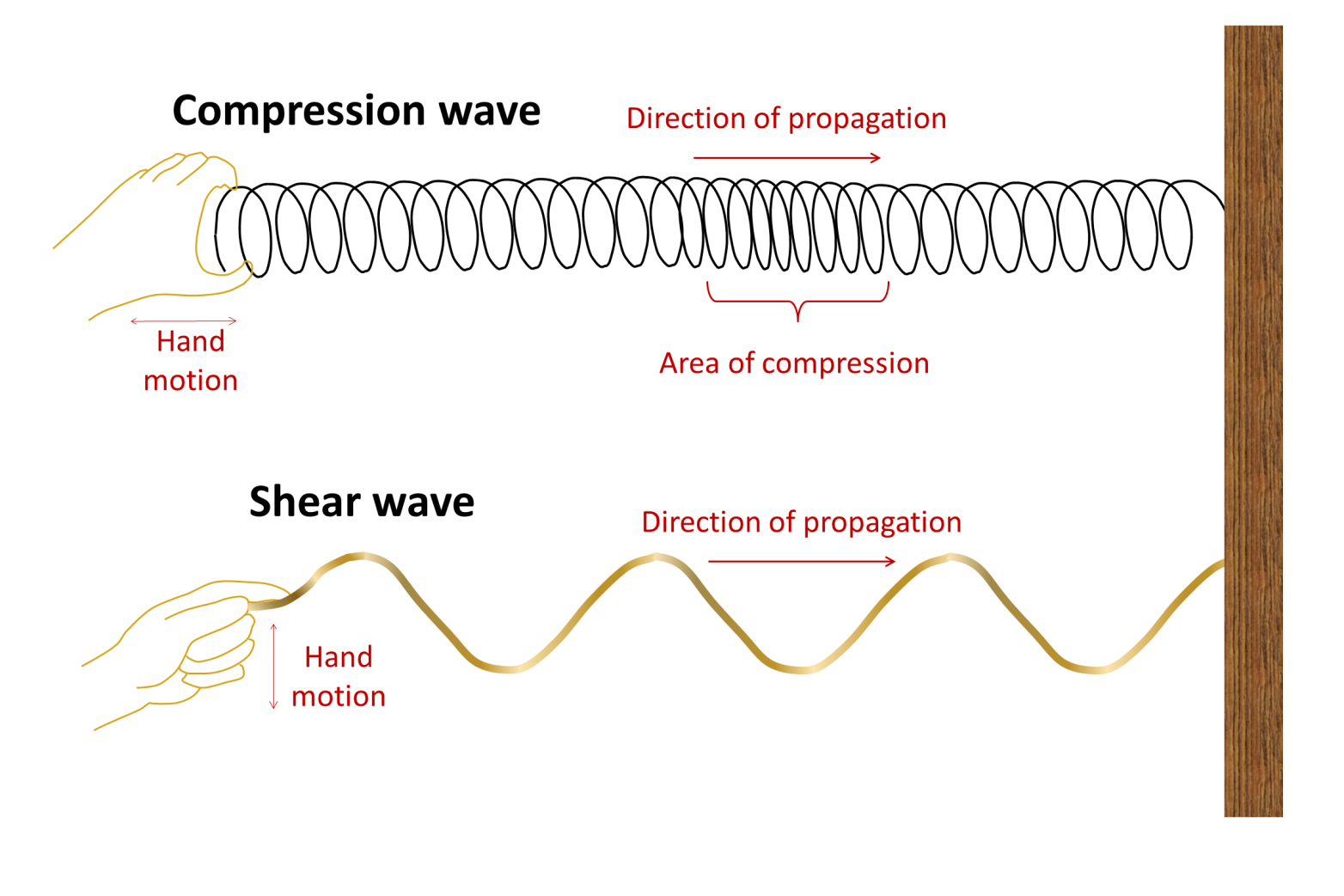
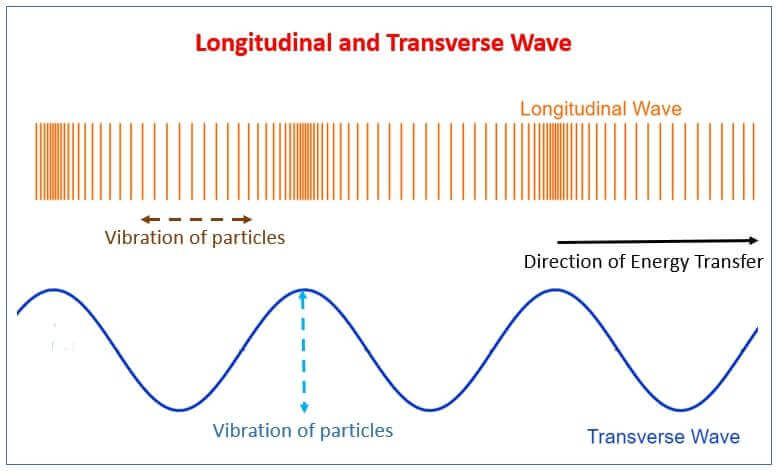
6)Rayleigh waves These are surface waves that can cause vertical motion;Wave wāv 1 a uniformly advancing disturbance in which the parts undergo a change in direction, such as a progressing disturbance on the surface of a liquid 2 variation in the transmission of electromagnetic energy, especially the periodic change in direction of a reading on a monitoring device A wave the wave on a His bundle electrogram that
S wave shadow zone definition
S wave shadow zone definition-View Notes ESSE 1010 MidtermTerm Definition What is the approximate shape of our solar system? Match the term on the left with its definition on the right Term Definition 4 Seismic shadow zone a A process used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake 5 Triangulation b A surface wave that causes horizontal motion 6 Rayleigh waves c Areas on the earth s surface where waves traveling through the earth don t arrive due to refraction 7

Earthquake Glossary
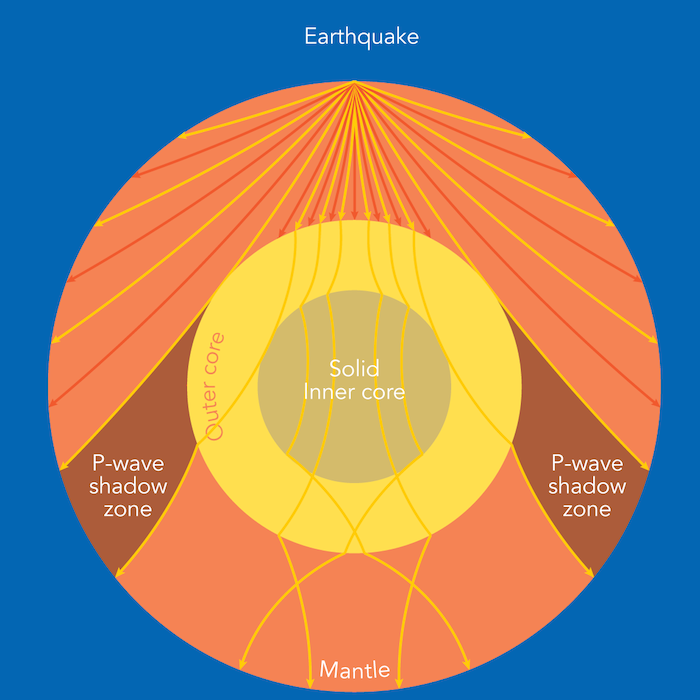
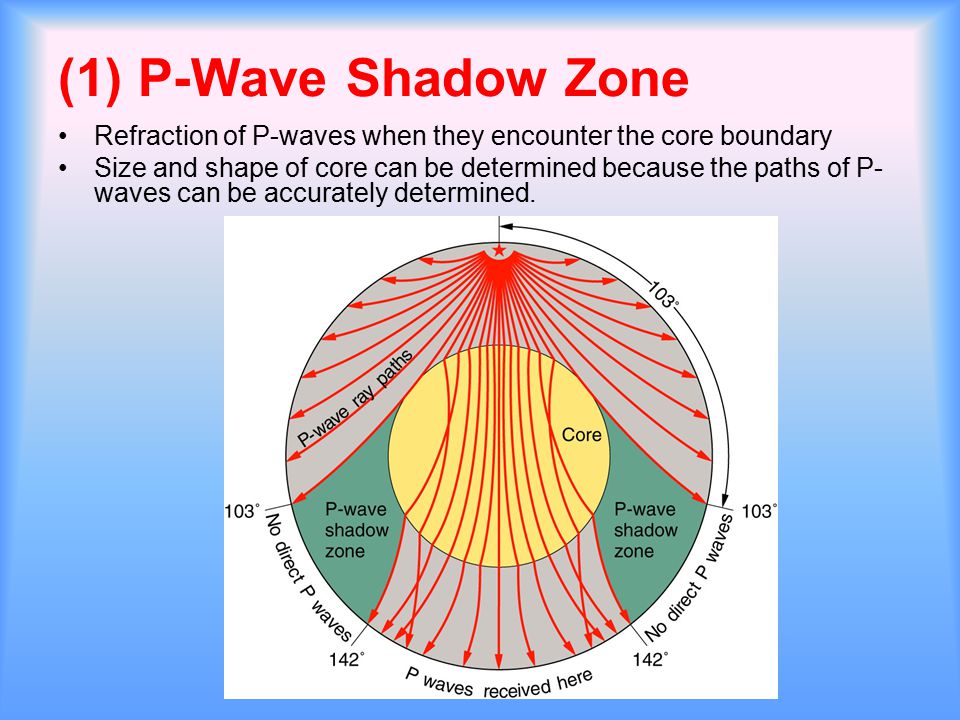
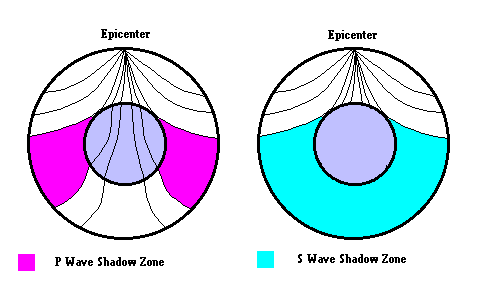
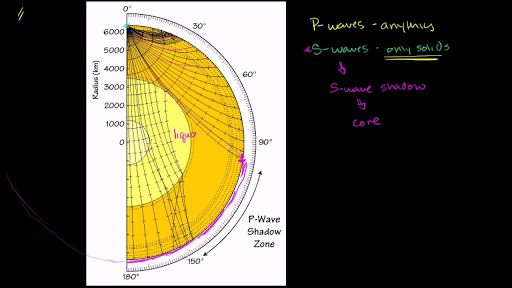
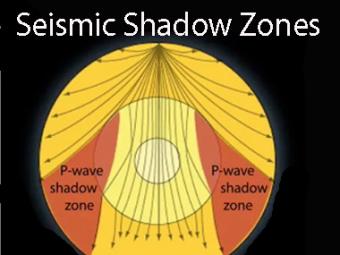
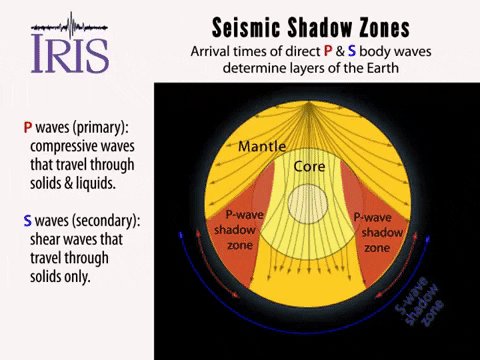
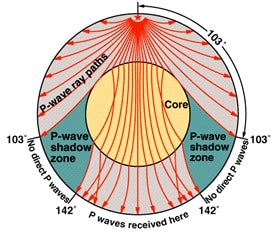
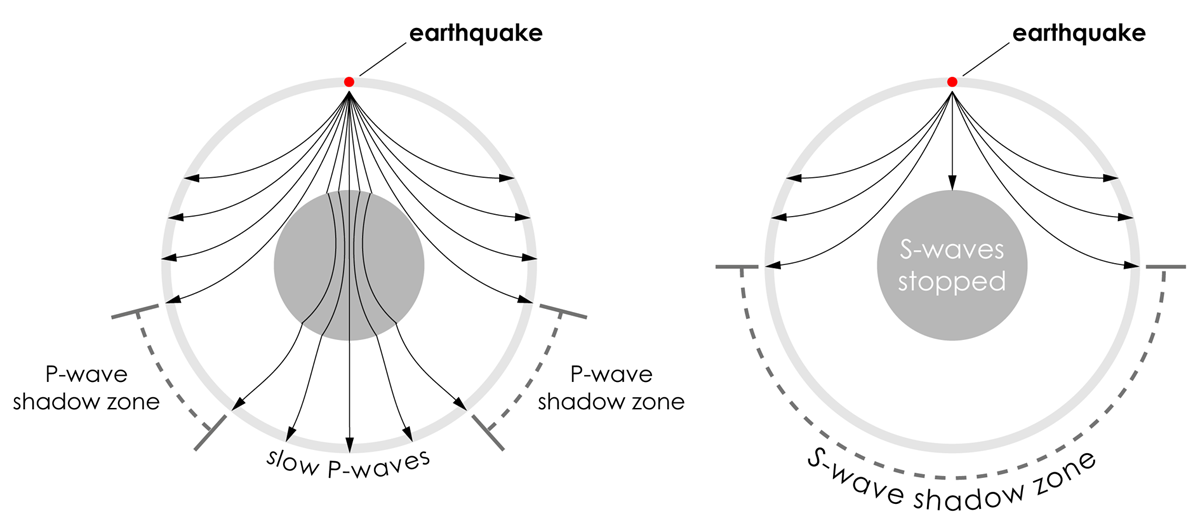
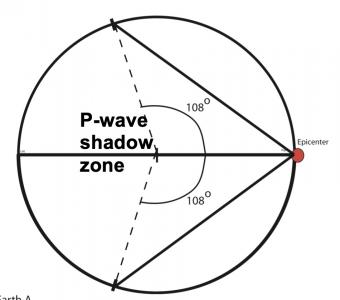
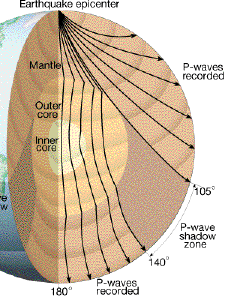
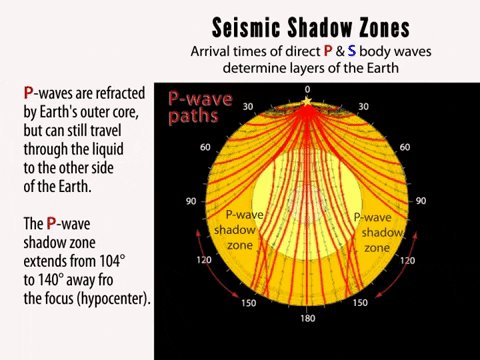
A Pwaves are absorbedShadow zone of an earthquake;Seismic shadow zones are areas away from the epicenter of an earthquake that seismic waves are blocked or refracted away from This lesson will cover
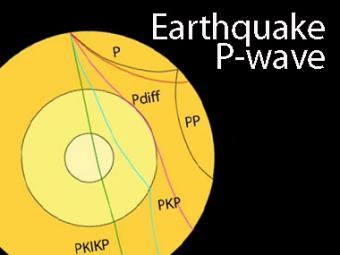
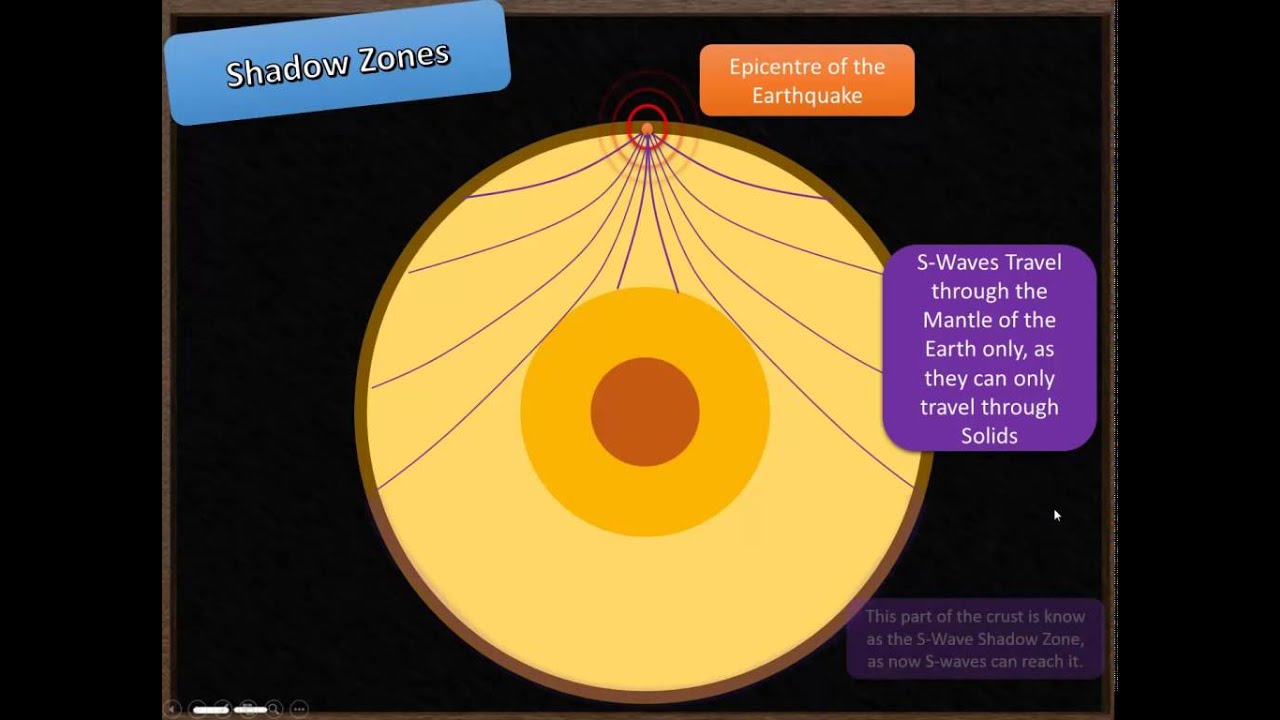
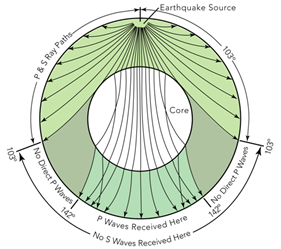
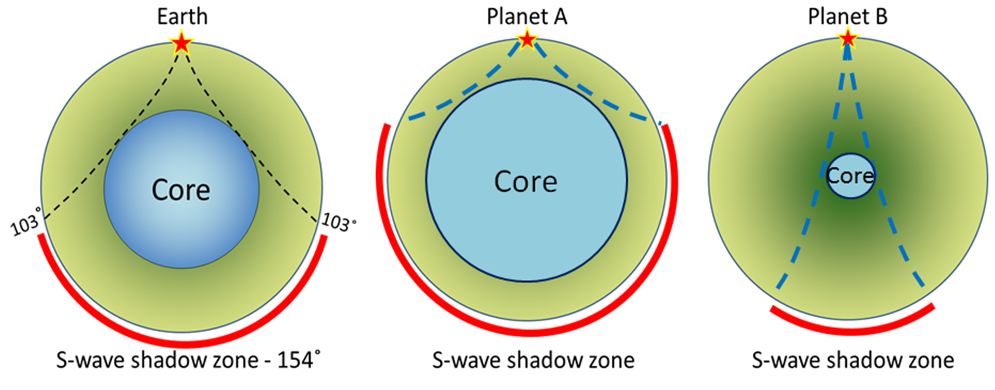
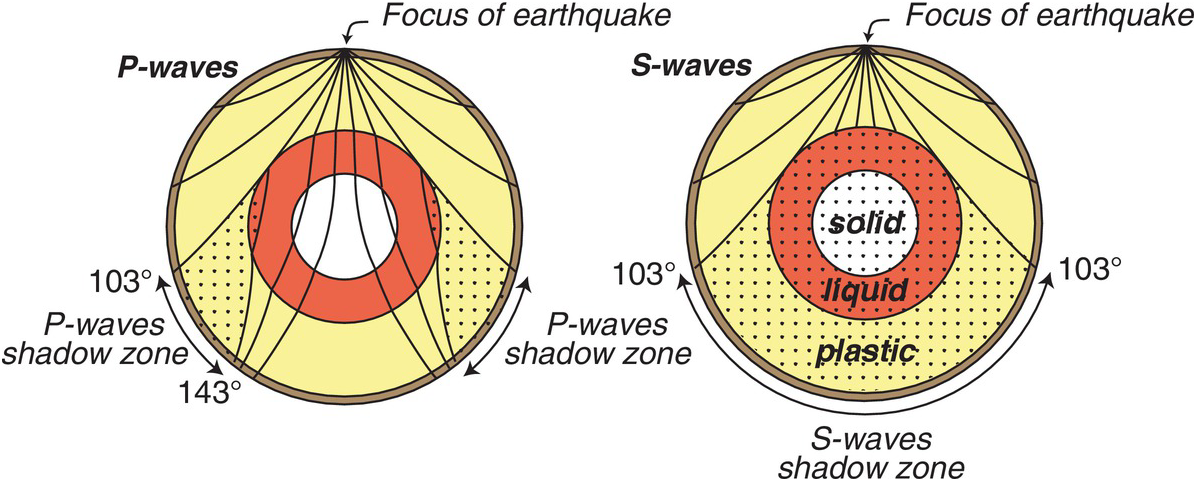
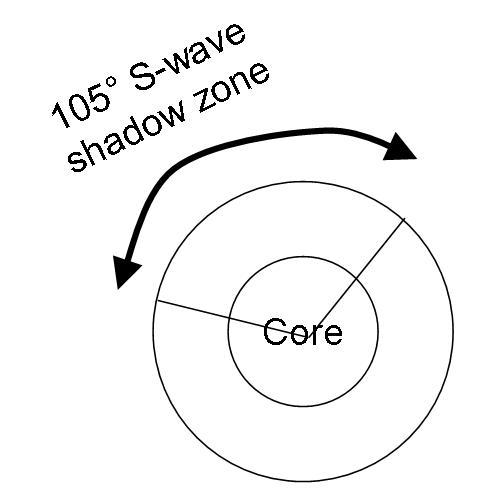
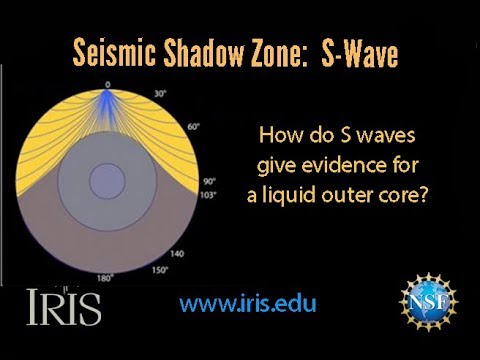
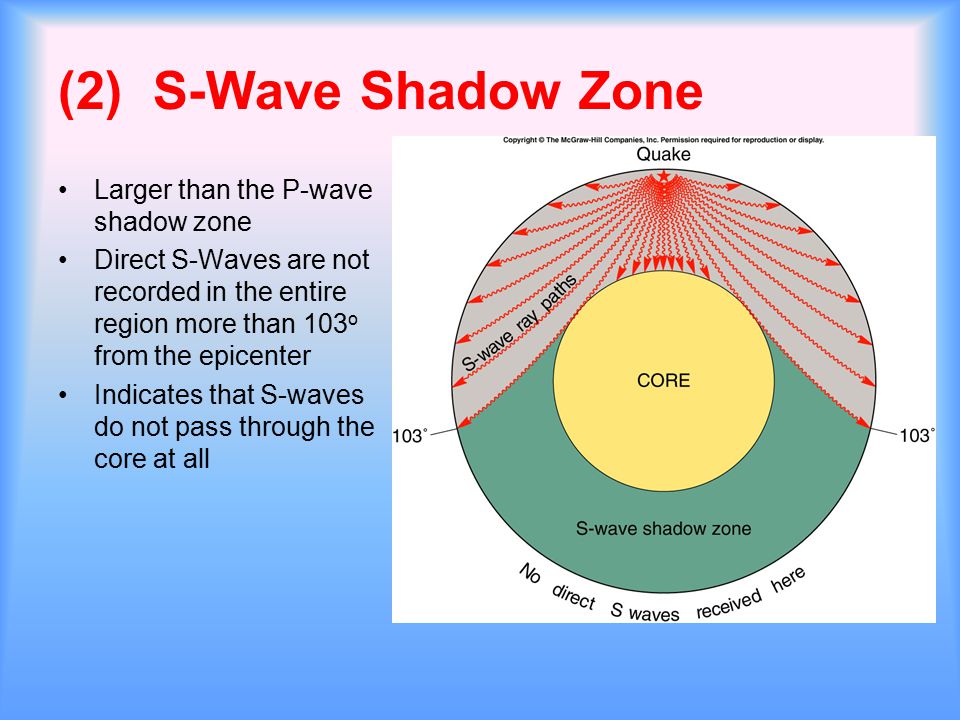
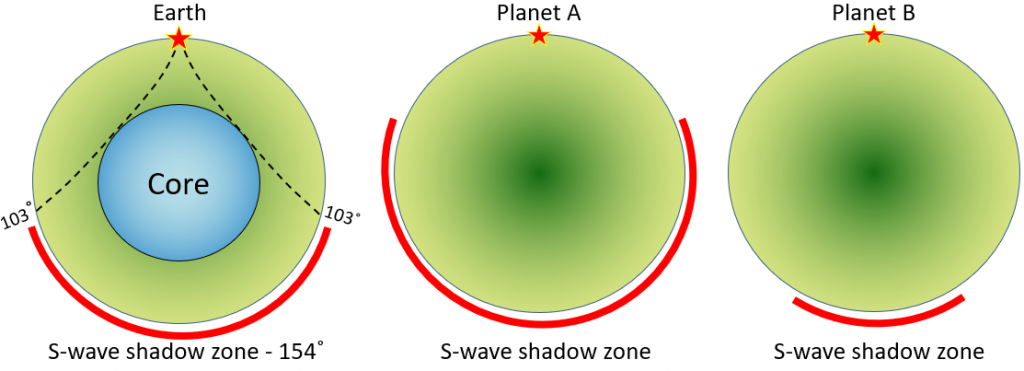
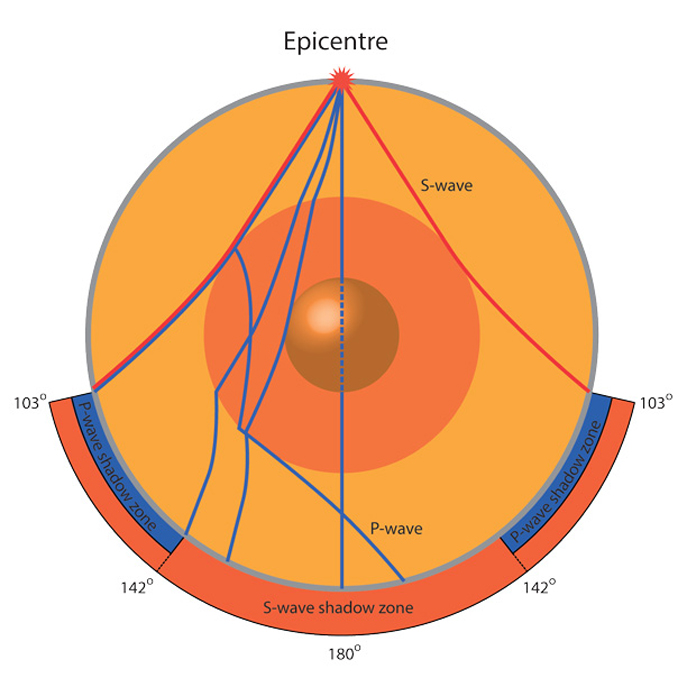
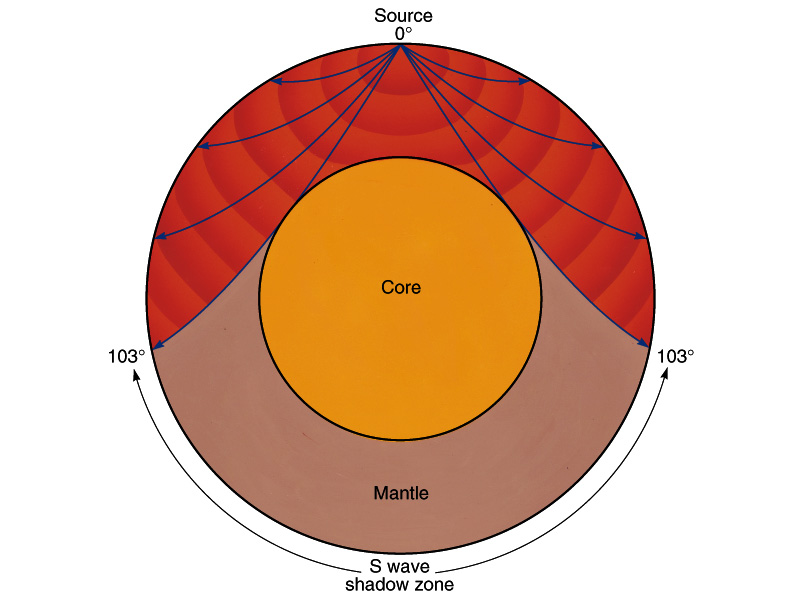
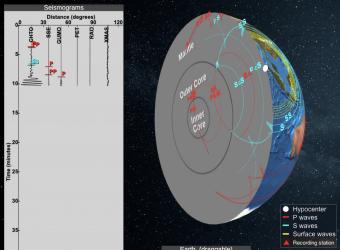
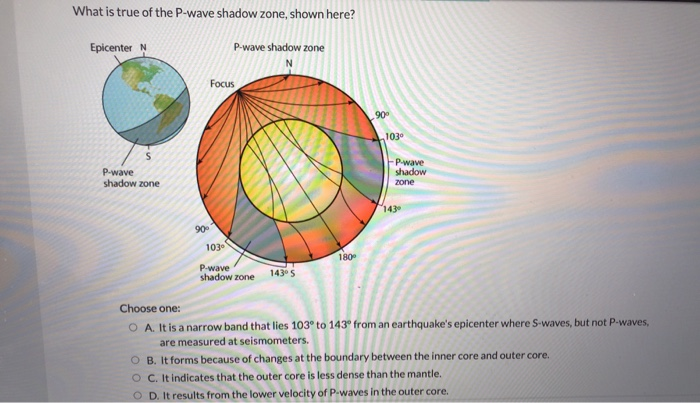
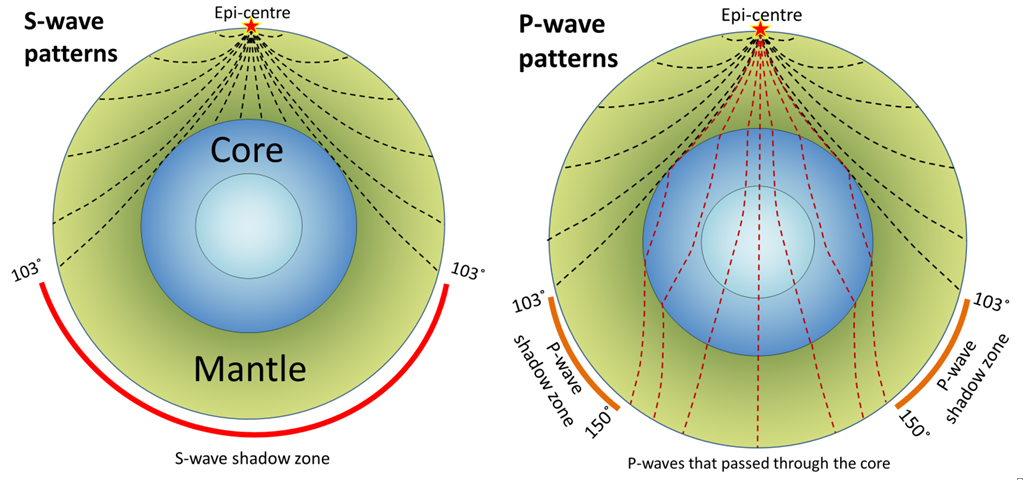
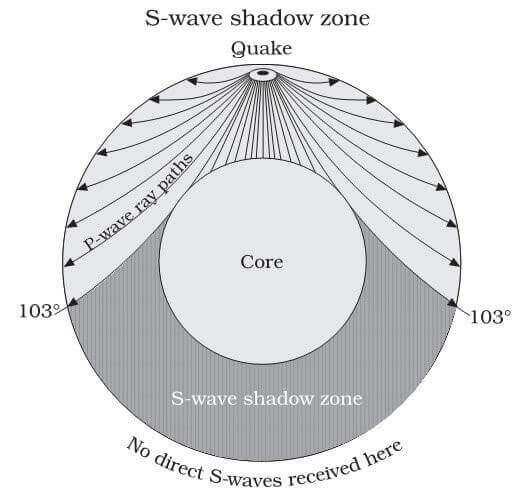
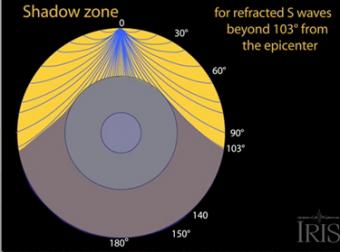
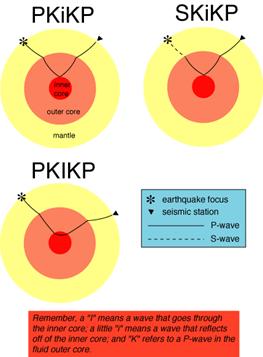
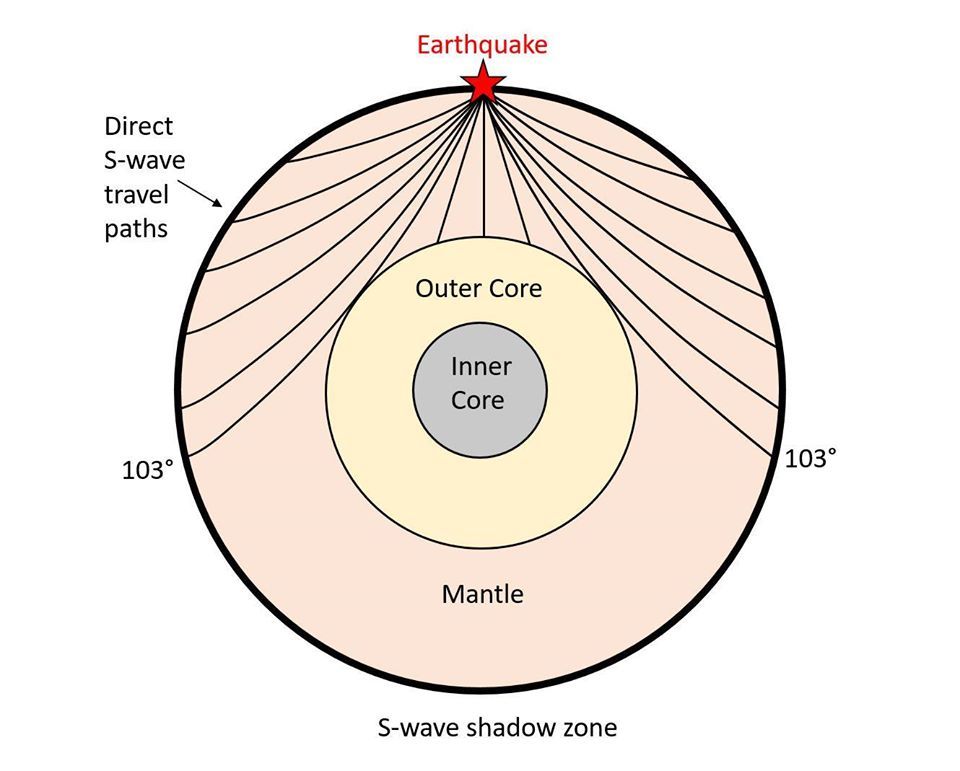
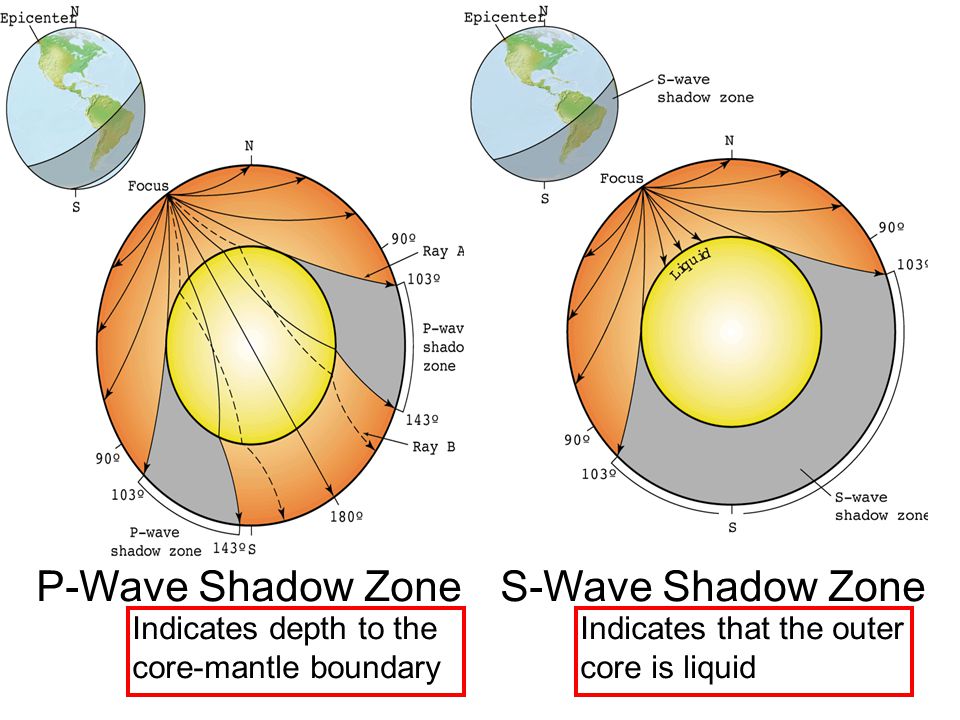
An Swave shadow zone is formed as seismic waves travel through the earth's body Which of the following statements does this Swave shadow zone indicate? S wave shadow zone range S wave shadow zone rangeThe Swave shadow zone is evidence that a) The outer core is liquid b) The outer core is composed of iron and nickel oxides c) The inner core is solid d) It is very hot near the coreThe Swave shadow zone occurs because no Swaves reach the area on the opposite side of the Earth from the focus Since no direct SwavesSwaves do not travel through liquids — they are stopped at the CMB — and there is an Swave shadow on the side of Earth opposite a seismic source The angular distance from the seismic source to the shadow zone is 103° on either side, so the total angular distance of the shadow zone is 154° We can use this information to infer the depth to the CMB Pwaves do travel through
S wave shadow zone definitionのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「S wave shadow zone definition」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |
The Swave shadow zone occurs because no Swaves reach the area on the opposite side of the Earth from the focus Since no direct Swaves arrive in this zone, it implies that no Swaves pass through the core This further implies the velocity of Swave in the core is 0 In liquids μ = 0, so Swave velocity is also equal to 0 From this it isShadow zone area of detection Figure 1 Diffraction of electromagnetic waves A radio wave that meets an obstacle has a natural tendency to bend around the obstacle as illustrated in the figure The bending, called diffraction, results in a change of direction of part of the wave energy from the normal lineofsight path This change makes it possible to receive energy around the edges of
Incoming Term: s wave shadow zone definition,



